- Free First Class Delivery
- Buyer Protection
- Secure Online Shopping
- Healthcare Professional? Click here
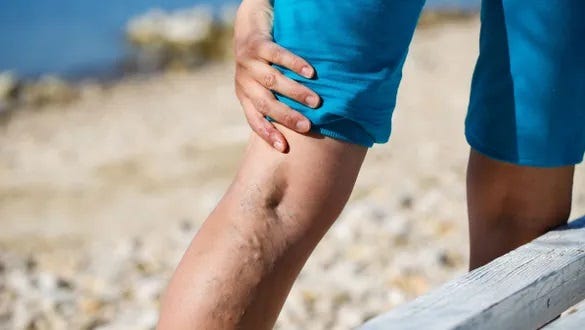
Inflammation of the vein (phlebitis)
Local and painful


Categories
What is vein inflammation?
Vein inflammation is also known as phlebitis. Inflammation of the vein is when blood clots forms in the superficial vein near the wall surface (usually a varicose vein) or when the vein wall is damaged (due to trauma). This occurs mostly in the region of the leg and can be detected in the thigh, calf, knee, foot or ankle.
Superficial phlebitis is restricted locally and can be painful. The effected varicose vein and surrounding skin will often present as red, warm and often the area will be swollen. You will need to contact your local nurse or doctor to seek advice and treatment. If untreated, it may spread and cause pain lasting several weeks or if a blood clot is present this could move into the deeper vein, causing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Causes and risk factors for vein inflammation
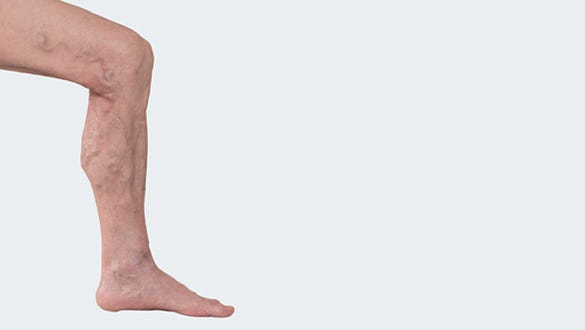

A slower blood flow is the most common cause of the vein inflammation. It leads to inflammatory reaction on the weakened vein wall that is often predisposed by varicose veins. The inflammation can also occur if the vein is squeezed together over long periods, this could be caused by tight clothing.
Other common reason for vein inflammation in the leg is from an injury such as an insect bite.
Recognising vein inflammation: Symptoms and signs
- Pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Warmth to the area
- Sensation of pressure
- Hardening of the vein


Preventing vein inflammation
You can take control yourself to prevent vein inflammation and other venous conditions from arising.
Some tips:
- Basic therapy: Wear medical compression stockings on a daily basis if your legs are prone to varicose veins.
- Exercise: Avoid long periods of standing and sitting, and do vein exercises to activate your venous pump
- Sport: Activities such as swimming, hiking and Nordic walking activate your veins.
- Drink plenty of water: A lack of fluids makes the blood thicker, meaning that your risk of blood clots increases.
- Go to your doctor: Have your varicose veins treated.
- Risk factor: Take care of your health: Give up smoking because smoking alters the vascular walls.
Products from medi
Treatment of vein inflammation
The treatment for vein inflammation will depend on its type and how serious it is. Your nurse or doctor will assess you to establish if the inflammation is superficial or deep.
Superficial vein inflammation can be treated easily are home by the following:
- Cold compress over the effective area
- Leg elevation to help reduce the swelling
- Wearing your prescribed compression hosiery can help to reduce the swelling.
- Keeping active to increase the blood circulation
- Analgesic (anti-inflammatory)
Superficial vein inflammation that is diagnosed and treated will often subside within a few days and usually without any complications.
What happens when vein inflammation is left untreated?
Deep vein inflammation can result in a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and will require further examination and treatment. Your nurse or doctor will want you to have a scan to identify if there is a blood clot present.
Your Doctor or Clinician decides on your treatment therapy after diagnosing your condition. They will then prescribe the relevant wound care therapy products to meet the patient’s individual treatment plan.